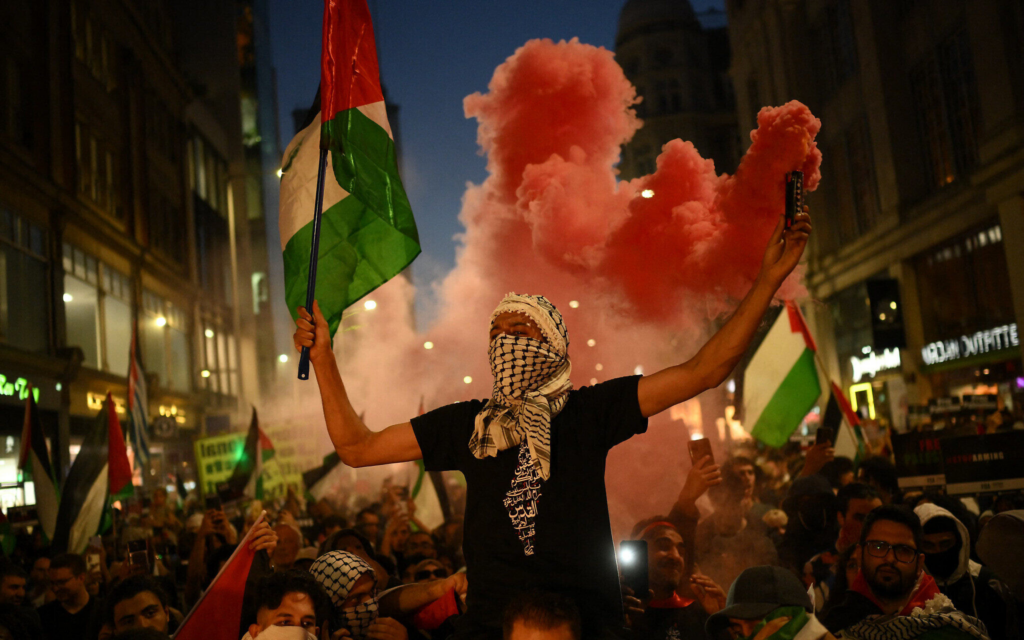
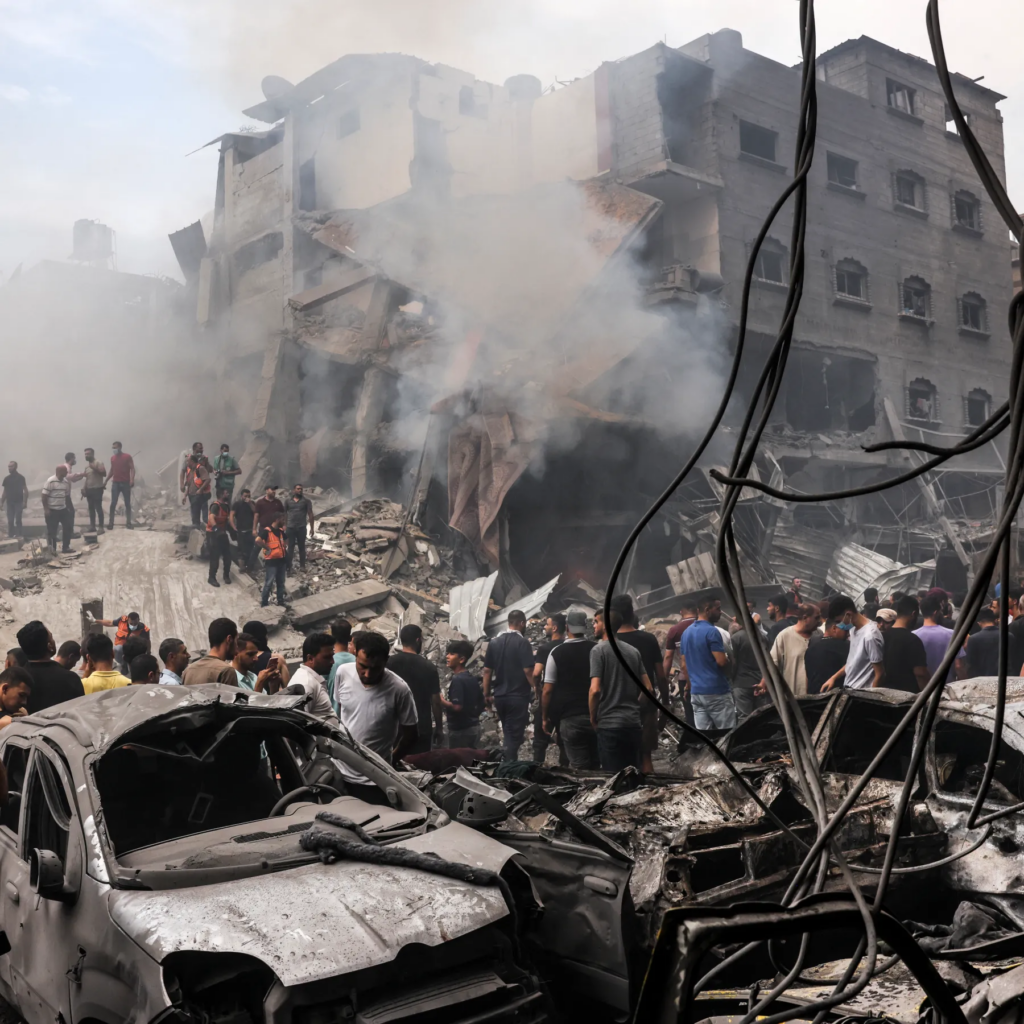
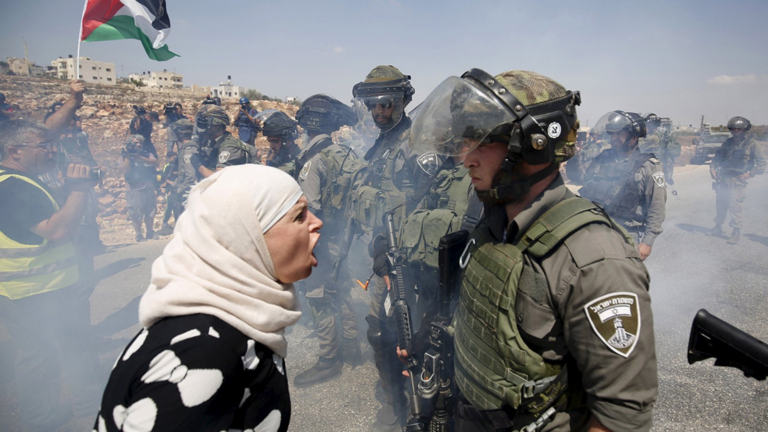
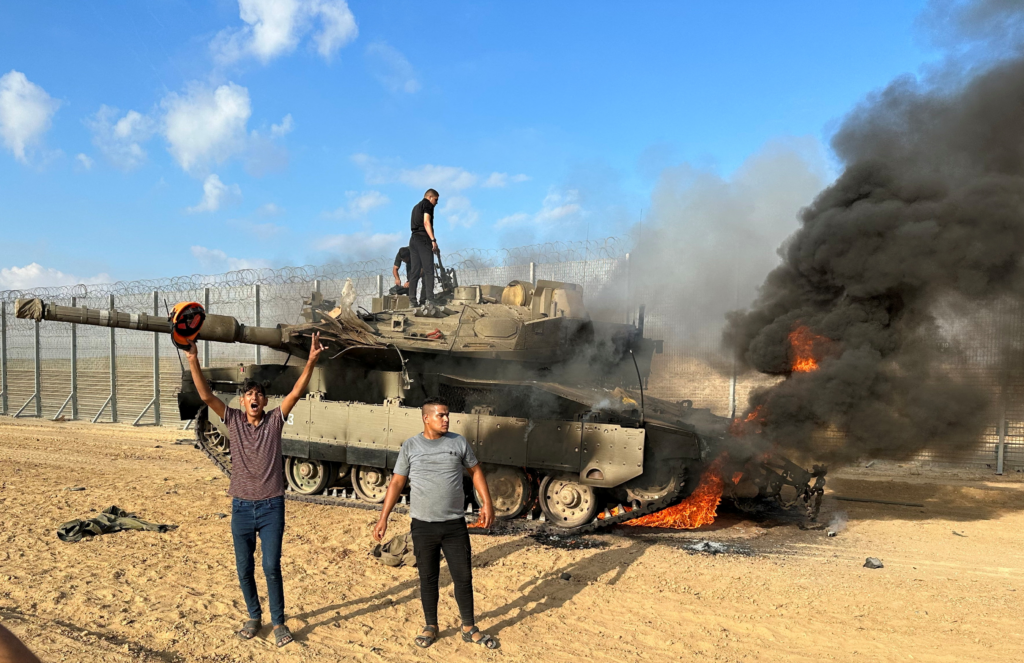
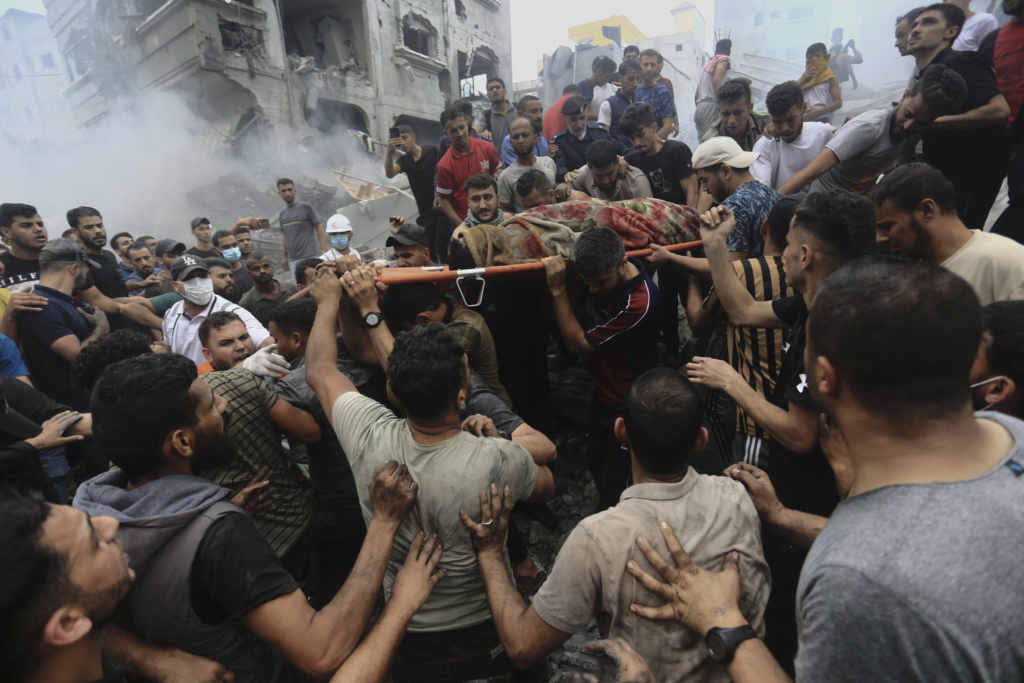
Why I am writing this column is to try and give a place for you to start. Many other journalists have written and broadcast on this very subject. As a journalist, it is our job to make sense of the world. I would argue that not all summaries are ‘equal’. Unfortunately, yet unsurprisingly, nothing about what is happening is easy or simple. If someone seems to think it is, then they’re not doing a good job.
Whether you believe journalism is a noble pursuit or not, I do believe it should strive for truth. I’m not sure we’re seeing balance or clarity in regard to this conflict, considering there are so many politics, faiths and emotions rolled into it. I will try my best to offer some guidance that I have used to make sense of what is happening in Gaza, which is both so important yet so far removed from our lives.
(Hi)stories
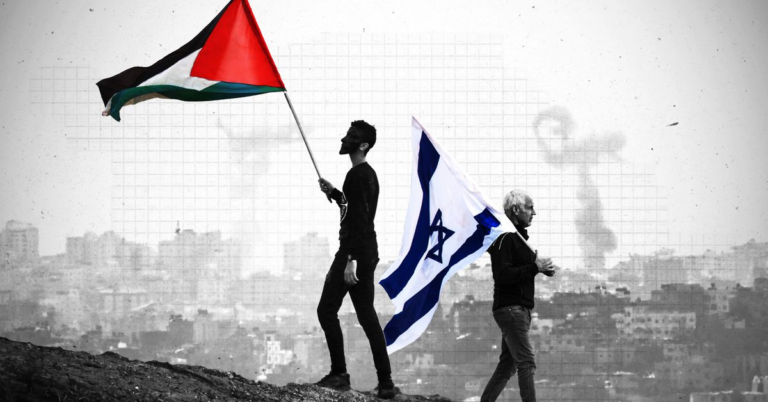
While the Israel-Hamas conflict is very current, Israel and Palestine have a long and complicated history. Despite what some articles would have you believe, tensions in this region are decades old. And if you think that it has nothing to do with ‘us’ – read on just a little further.
If you ask people where to date the start of the conflict, some may go back even to ancient history. I recommend looking at the aftermath of World War Two. In 1947, the United Nations voted to partition the British Mandate, Palestine into two states. One Jewish, and One Arab. Why this was proposed in the first place is a spider’s web of declarations and treaties. The reason it was a British Mandate is thanks to the First World War as the territory was conceded by the Ottoman Empire.
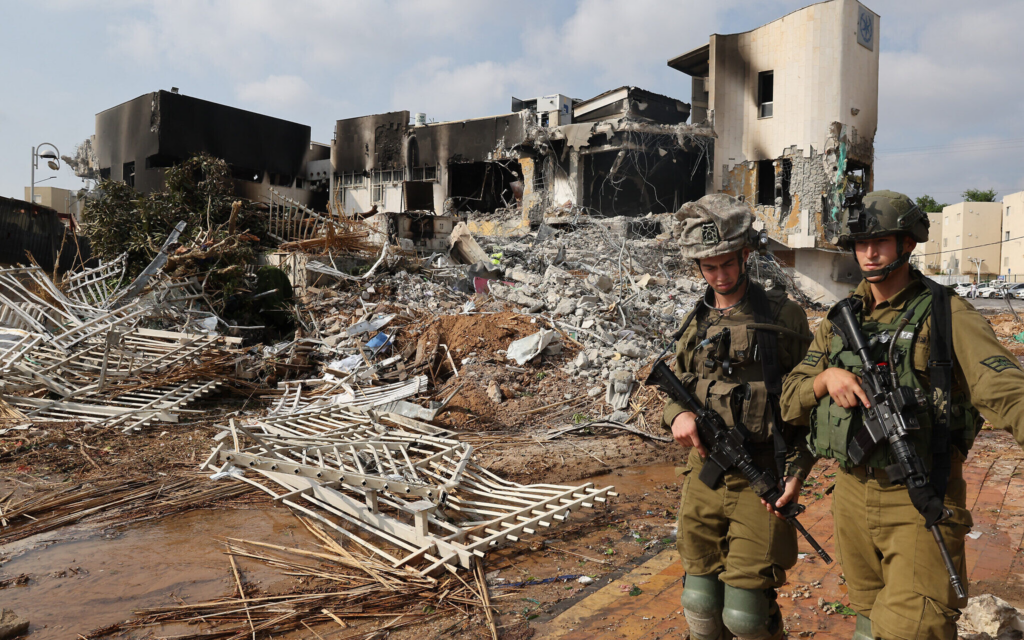
Evidently, there are many sides and aspects to the history. Instead, perhaps look at the stories. The horrific ones we are reading about currently from this current war. Plus those of Palestinians experiencing occupation and Israelis first moving to the state of Israel. If you feel you must decide a ‘right’ or ‘wrong’ for this conflict, I would urge you to hear people’s voices first as they are the ones who are affected by this historical conflict every single day.
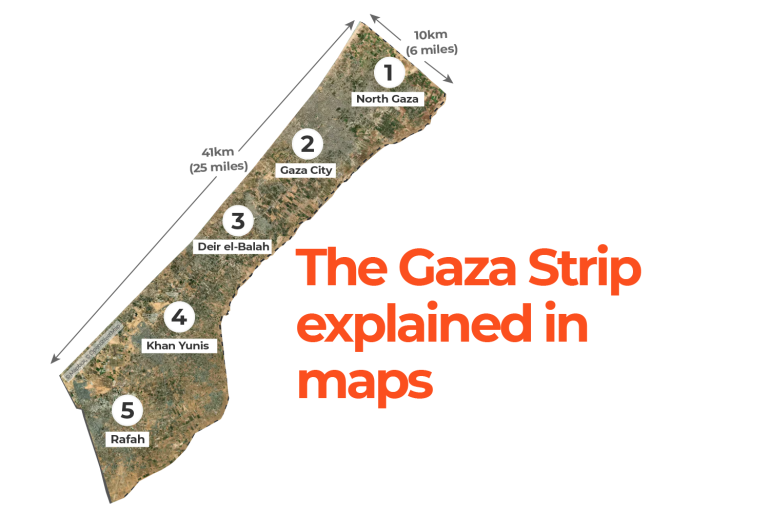
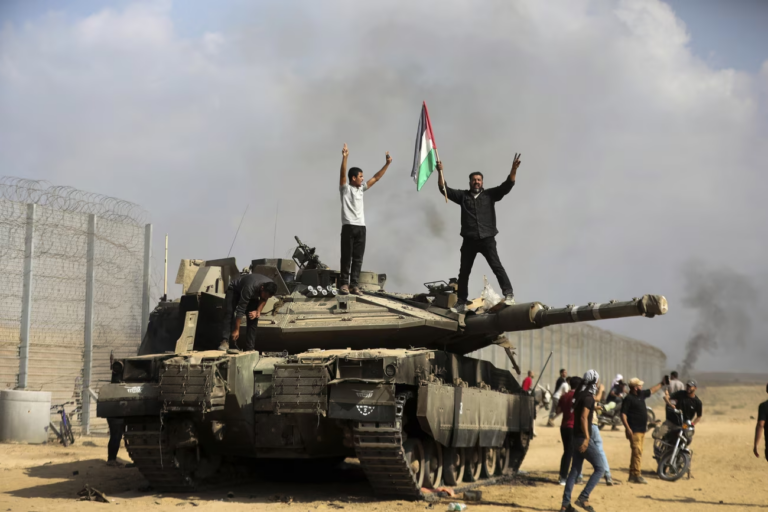
The Gaza Strip occupies land along the Mediterranean Sea. It is physically isolated from the remaining territory of Palestine, and similarly, the governing entities are different. Hamas was elected in 2007 and no elections have taken place since then, while the remaining areas are under the PLO or Fatah. Israel and Palestine are home to several religious and holy sites which means the land itself is perhaps of greater value to some. However, even a map is political. Thanks to wars, and occupation the shape of Israel has changed over time, and in parts is still undefined, some feel certain maps support the arguably illegal occupation undertaken by Israel.
Faith
This conflict and the region will often be simplistically divided into Islam and Judaism. But the picture is far more complex. Christians although a minority are present in the region. Expressing support or concern for a people on either ‘side’ should not be considered Islamophobic or antisemitic. When people throw around extreme language, they are trying to divide people and squash debate. You can promote peace while still believing that a group or state’s interest should be heard.
International Politics
While Palestine is described by many as a state, it is not. 138 of the 193 UN member states have recognized Palestine as a state. Of the G20, Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Mexico, the United Kingdom, and the United States all have not formally recognized Palestine, yet most have expressed support for a two-state solution. Many articles and news stories speak as is Palestine is a country, when in fact it is not. Ensure that what you read is able to balance these facts when they make their arguements.
Is peace possible? Very few people will know what peace looks like on both sides. Pay attention to the language people are using. Are they war-making or peacebuilding? To prevent further catastrophe, we must amplify the experts looking for a long-lasting resolution. We have done a disservice to the region to allow a conflict to be unresolved for so long. I’m not sure if or when it will end but peace is deserving to all civilians living in the region.